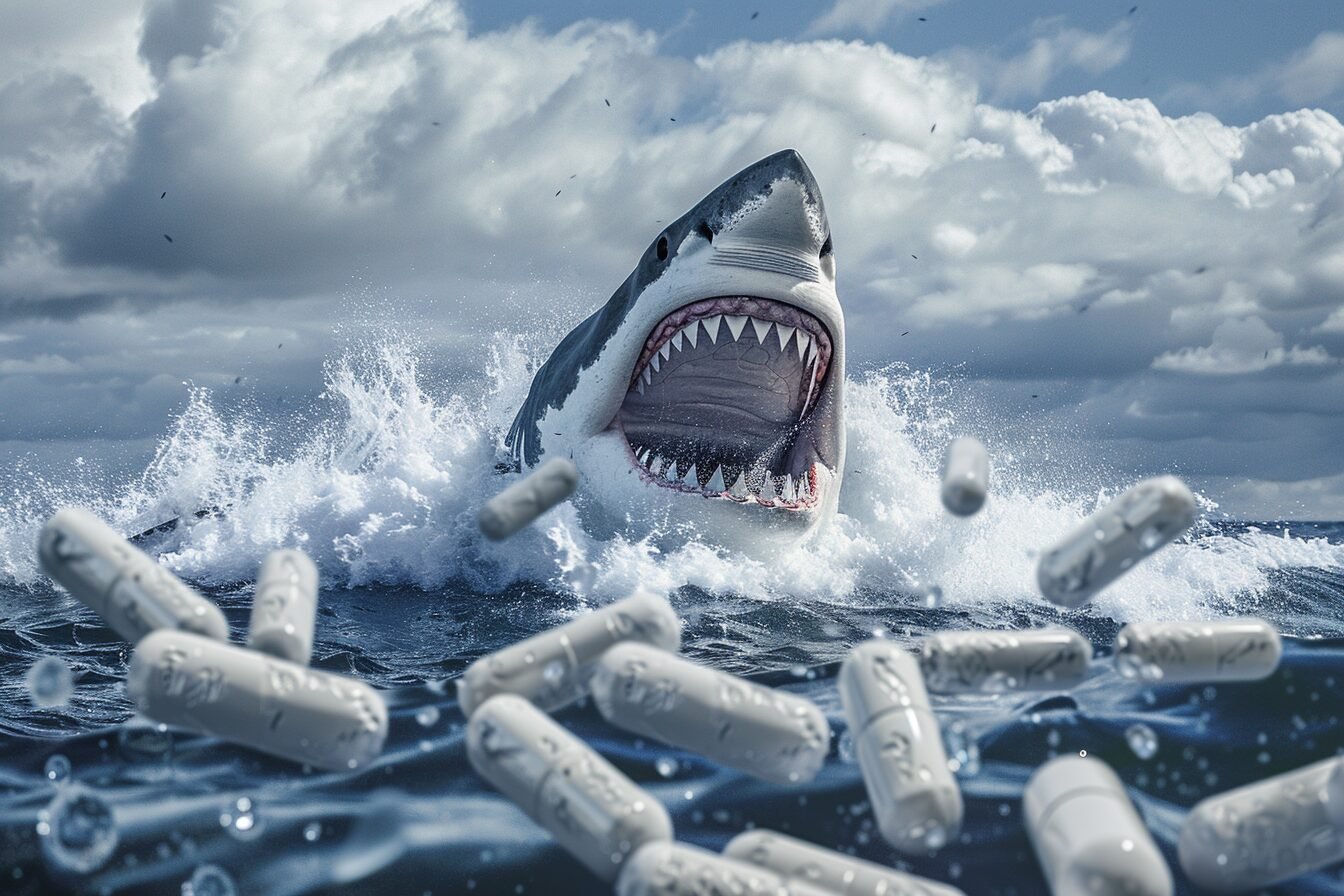
Sharks off the coast of Brazil’s party city Rio de Janeiro have tested positive for cocaine.
The predators were consuming the potent stimulant due to its continuous release from inadequate sewage treatment facilities and clandestine refining operations, scientists wrote in a study published in Science of The Total Environment.
Some may also have attacked bricks of cocaine which traffickers had lost at sea off the coast of Brazil, one of the world’s largest markets for the drug. Of the 13 specimens of Brazilian sharpnose shark scientists tested over almost three years, all presented cocaine in their muscle and liver tissue, according to the study by the Oswaldo Foundation Cruz, an institute of science, technology and health.
The drug was found in all 13 wild Brazilian sharpnose sharks tested, with a concentration as much as 100 times higher than previously reported for other aquatic creatures.
Scientists collected the samples between September 2021 and August 2023 as they monitored environmental impacts of pollution on marine life. Rachel Ann Hauser-Davis, a biologist from the IOC Environmental Health Assessment and Promotion Laboratory, said that because sharks were predators, they were central figures in the food chain and were considered “sentinel species” that could provide early warnings about environmental threats to humans.
The scientists did not list what effects cocaine and other recreational drugs might have on sharks, although other studies have shown brown trout can become addicted to methamphetamine.
Scientists elsewhere have documented that other pollutants like antidepressants, heavy metals, and birth control medications are also making their way into rivers, lakes and oceans.