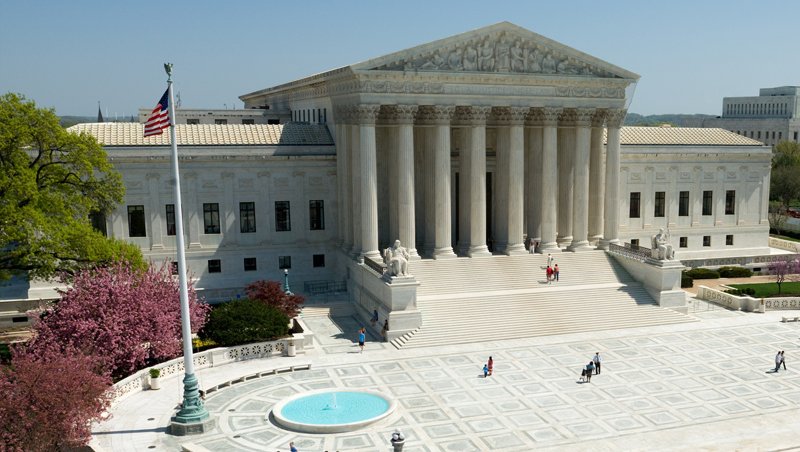
The United States judicial system, with the Supreme Court at its apex, is a cornerstone of American democracy. Its decisions reverberate not only within the country’s borders but also across the globe, influencing legal standards and norms worldwide. This article delves into the structure of the federal judiciary, the pivotal role of the Supreme Court, significant Supreme Court decisions, the balance of judicial independence and accountability, and the global influence of the US judicial system.
The United States federal judiciary is a complex system designed to interpret and apply laws within the framework of the U.S. Constitution. At its core, the federal judiciary is structured into three main tiers: the district courts, the courts of appeals, and the Supreme Court. District courts serve as the trial courts where cases are initially filed and heard. They handle both civil and criminal cases under federal jurisdiction. Above the district courts are the courts of appeals, which review decisions made by district courts. These appellate courts are divided into 13 circuits, each serving a specific geographical area.
At the pinnacle of the federal judiciary is the Supreme Court, the highest court in the land. It holds the ultimate authority in interpreting the Constitution and serves as the final arbiter in disputes involving federal law. The Supreme Court is composed of nine justices, including one Chief Justice and eight Associate Justices, all appointed by the President and confirmed by the Senate. This hierarchical structure ensures that federal laws are uniformly interpreted and applied across the United States, maintaining a consistent legal framework.
The Supreme Court of the United States plays a critical role in the American judicial system. It not only serves as the final court of appeal but also holds the power of judicial review, enabling it to invalidate laws and executive actions that it deems unconstitutional. This power, established in the landmark case of Marbury v. Madison (1803), allows the Court to ensure that all branches of government adhere to the Constitution. The Supreme Court’s decisions are binding on all lower courts, setting precedents that shape future legal interpretations and public policies.
Beyond its appellate function, the Supreme Court also has original jurisdiction in certain cases, such as disputes between states or cases involving foreign diplomats. However, its most significant impact comes from its ability to set legal precedents through its rulings. These decisions can redefine laws, influence legislative actions, and shape societal norms. For example, the Court’s ruling in Brown v. Board of Education (1954) not only dismantled the legal basis for racial segregation in public schools but also ignited the broader Civil Rights Movement, highlighting the Court’s profound influence on American society.
Throughout its history, the Supreme Court has rendered numerous landmark decisions that have had far-reaching implications for American society and governance. One such decision is Roe v. Wade (1973), where the Court recognized a woman’s constitutional right to privacy, effectively legalizing abortion nationwide. This ruling not only transformed reproductive rights in the United States but also sparked ongoing debates and legal battles over the extent of these rights.
Another pivotal decision is Obergefell v. Hodges (2015), which legalized same-sex marriage across the United States. By recognizing that the Constitution guarantees the right to marry to same-sex couples, the Supreme Court significantly advanced LGBTQ+ rights, setting a precedent that influenced legal standards in other countries. Similarly, the decision in Citizens United v. Federal Election Commission (2010) dramatically altered the landscape of campaign finance by ruling that corporate funding of independent political broadcasts in candidate elections cannot be limited under the First Amendment, thereby increasing the influence of money in American politics.
Judicial independence is a cornerstone of the American legal system, ensuring that judges can make decisions free from political pressure or influence. The lifetime tenure of federal judges, including Supreme Court Justices, underscores this principle, allowing them to rule based on their interpretation of the law rather than on popular opinion or political considerations. This independence is critical for maintaining the integrity and impartiality of the judiciary.
However, this independence is balanced by mechanisms of accountability. Federal judges can be impeached and removed from office for misconduct, ensuring that they adhere to high ethical standards. The Senate confirmation process for judicial appointments also serves as a check, allowing for scrutiny of a judge’s qualifications and judicial philosophy. Additionally, the publication of judicial opinions provides transparency, enabling the public and legal community to critique and analyze court decisions. These measures collectively help to maintain a judiciary that is both independent and accountable, preserving public trust in the legal system.
The decisions of the U.S. Supreme Court often resonate beyond American borders, influencing legal standards and norms worldwide. As one of the most prominent judicial bodies, the Court’s rulings are closely watched by legal scholars, practitioners, and policymakers globally. For instance, the principles established in Brown v. Board of Education have been cited in international human rights cases addressing racial discrimination and educational equality.
Moreover, the Supreme Court’s interpretation of constitutional rights, such as freedom of speech and the right to privacy, has influenced the development of similar legal protections in other democracies. The Court’s decisions on issues like same-sex marriage and reproductive rights have provided legal frameworks and precedents that other countries have considered when shaping their own laws. For example, the Obergefell decision has been referenced in debates and legal rulings on same-sex marriage in countries such as Australia and Taiwan.
The U.S. Supreme Court’s global influence is also evident in its role in shaping international human rights law. Its interpretations of due process, equal protection, and other fundamental rights contribute to the broader discourse on human rights, providing a benchmark for legal standards worldwide. Thus, the Supreme Court not only impacts domestic policy but also plays a significant role in the evolution of global legal norms.
The U.S. judicial system, with the Supreme Court at its apex, serves as a crucial guardian of constitutional principles and legal integrity. Its decisions shape the legal landscape of the United States, influencing everything from civil rights to campaign finance. The Court’s rulings often extend beyond national borders, setting precedents that impact global standards and norms. Judicial independence and accountability ensure that the judiciary remains a fair and impartial arbiter of justice. As the world continues to evolve, the influence of the U.S. Supreme Court on both domestic and international law will undoubtedly persist, reinforcing its role as a pillar of the global legal order.